The Best Supplements For Beautiful Skin
What if beauty was as simple as popping a pill? It seems like almost daily we encounter the latest pill, beverage, powder, or cream that promises to have found a way to bottle the fountain of youth — and at a steep price.
But what ingredients and supplements have really proven to boost the vitality and beauty of our complexions, beyond the vitamins and minerals we already consume in our diets? Which ones are just a lot of hype? Is popping a pill always the right choice, or would a topical supplement lead to better results? Here are your answers!
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is integral to the health of our skin, and is a key ingredient in many topical anti-aging serums and lotions. Vital to the formation of collagen, the building block of skin, vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that is essential for wound healing, and can help the body to fight the damages of UV exposure. But will it keep you looking beautiful? According to the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, it will. A 2008 study on over 4000 middle-aged British women showed that higher vitamin C intake was associated with less skin dryness and wrinkling.
Unlike most other animals, humans cannot synthesize vitamin C, meaning we need to ingest it regularly to not only receive its health benefits, but to prevent scurvy. Scurvy, the vitamin C deficiency that once plagued sailors at sea, can manifest within a month, and includes nasty symptoms like bleeding gums, weak connective tissues, visible capillary damage, skin thickening, poor wound healing, and eventually death.
The good news is, it's easy to get all the vitamin C we need, from eating a diet that includes fruits and vegetables. If your diet is not up to par, a vitamin C supplement is a wise idea to ensure you are getting the 75 mg per day recommended for adult women, especially smokers, who are recommended to consume an additional 35 mg daily.
Vitamin E
Vitamin C works even better in the body when teamed up with one of its favorite dance partners, vitamin E.
Vitamin E, found naturally in many seeds, oils, and nuts, acts as an antioxidant in the body, protecting our cells against free radical damage, and premature aging. While that may be enough to make you want to run right out and stock up on an oral vitamin E supplement, there is much debate as to whether oral vitamin E supplementation is healthy, with some studies linking it to cases of prostate cancer and death.
Applying it topically, however, is a completely different matter. Vitamin E, when applied topically, is absorbed by all the layers of the skin quickly, but when taken orally, could take up to seven days to reach the skin's layers. Topical vitamin E is mostly destroyed when exposed to sunlight, but when blended with vitamin C, the two antioxidants work synergistically to fight wrinkles, and protect against sun damage and skin cancer.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble compound also known as retinol. Retinol is essential for healthy vision, cell growth, and immune function. Deficiencies are rare, but vegetarians may be lacking due to the fact that vitamin A is only found in animal foods, though the body can also synthesize it from the beta carotene contained in vegetables. When it comes to skin health, the real wonders come from supplementing with vitamin A not orally, but topically.
Considered the gold standard in the anti-aging industry, retinol is available in prescription strength applications, which contain powerful doses of retinoic acid. Over the counter products are also available, which slowly convert to retinoic acid when applied to the skin. While results are faster with prescription formulas, they are famously irritating to the skin, so building up your tolerance to retinol by starting out with a drugstore brand may be a smart move.
But is all the trouble even worth it? You betcha. As Jennifer Chwalek, MD of Union Square Laser Dermatology, told Elle, "Prescription Retin-A and Tretinoin and over the counter retinols increase skin cell turnover and stimulate collagen synthesis. With consistent use of a topical retinol or Retin-A you can see improvement of fine lines, dark spots, texture, and tone."
Sound too good to be true? Here's the catch — the anti-aging effects of retinol don't happen overnight. Dermatologist, Dr. Kenneth Beer told the New York Times, "By 24 weeks, patients will see dramatic, marked improvements."
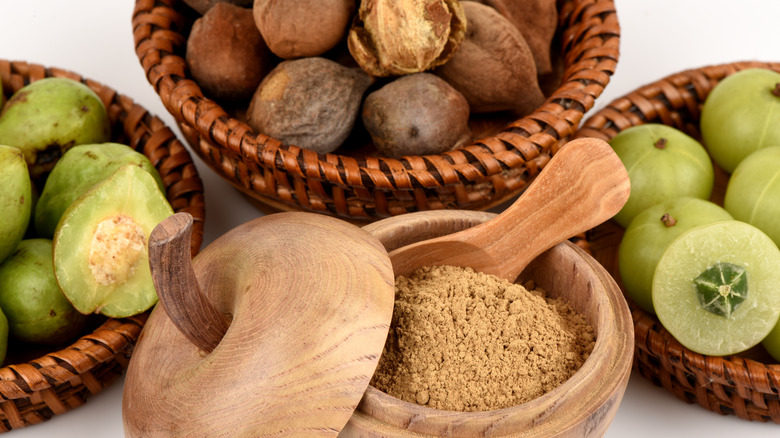
Triphala
Unless you are familiar with the mind-body science of Ayurveda, you may have never heard of Triphala. So what is it exactly? Triphala is a time-honored, Ayurvedic herbal remedy made up of the combination of three different plants: amalaki, haritaki, and bibhitaki. The Charaka Samhita, a classic Ayurvedic text, says that taking triphala daily can "make a person live for one hundred years devoid of old age and diseases."
According to Dr. Sheila Patel, medical director of the Chopra Center, triphala has traditionally been used as a detoxifier, rejuvenator, and mild laxative. Practitioners prescribe its use for a variety of ailments including obesity, allergies, liver problems, eye disorders, and skin inflammation. Scientific studies have shown that the synergistic qualities of these "three fruits" known as triphala do indeed produce a host of positive effects in the body, with triphala displaying anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antibacterial, and wound healing properties.
But will it improve your skin? Yes. Medical journal, Foods and Dietary Supplements in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease in Older Adults, reports, "Triphala provides cosmetic benefit and improves skin tone and complexion." The journal goes on to say that triphala can boost collagen production, prevent skin infections, and even combat the graying of hair.
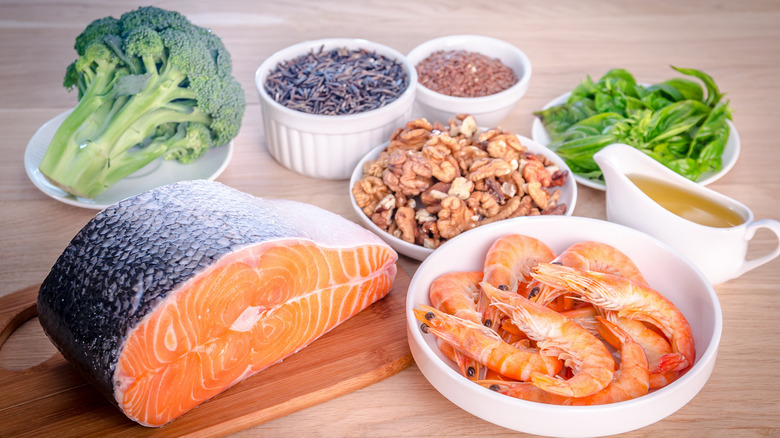
Omega 3
Omega-3s are the essential fatty acids found primarily in seafood, but also in some nuts, seeds, vegetables, and oils. Long touted as a nutritional miracle, omega 3 fatty acids have been scientifically shown to improve eye health, combat depression, fight autoimmune conditions, prevent age-related mental decline, and improve bone and joint health. Added bonus: they will also contribute to beautiful, glowing skin.
The omega-3 acid, DHA, is a key structural component of the skin, keeping the skin's cell membranes healthy and supple. EPA, another member of the omega-3 family, manages the skin's hydration system, prevents premature aging, combats acne, and halts the inflammation of hair follicles. But how much omega-3 do you need to enjoy its benefits?
The key lies in getting the proper balance of omega-3 acids with its fatty acid cousins, the omega-6s. While both are essential for our bodies, Americans get far too much omega-6 in our standard diet. Dr. Andrew Weil, M.D, and director of the Arizona Center for Integrative Medicine, says that we should aim to cut down on our intake of the omega-6s found in processed foods, and consume more of the omega-3s found in oily, wild fish. Two to three servings per week would be optimal. If supplementing, he advises seeking a product that offers a minimum of 700 mg of EPA, and 200mg of DHA, daily.
GLA oils
Though we likely already get too much omega-6 in our diet, there is one type of omega-6 fatty acid that is much harder to come by. Gamma-linolenic acid, or GLA is an omega-6 fatty acid found in hemp oil, spirulina, and the oils of plants like borage, black currant, and evening primrose. Dr. Weil says, "GLA is an effective anti-inflammatory agent that I recommend for arthritis, autoimmune disorders, premenstrual syndrome and for healthy growth of skin, hair, and nails." Weil advises supplementing with 500 mg of evening primrose oil or black currant oil twice per day, but recommends avoiding borage oil supplements, which could cause liver toxicity.
Dermatologist Elizabeth K. Hale, MD, agrees. She tells Glamour, "I love evening primrose oil. It's a plant extract that comes from the seeds of a wildflower. It's not only emollient (hydrating) but a powerful anti-irritant, which means it will have a significant anti-inflammatory effect on the skin."
As with many herbal supplements, patience is a virtue. A study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Science reported on the effects of daily evening primrose supplementation in a group of healthy adults. The researchers saw no benefits in the skin of the participants after four weeks, but reported a marked improvement in skin elasticity, firmness, and moisture after 12 weeks of use.
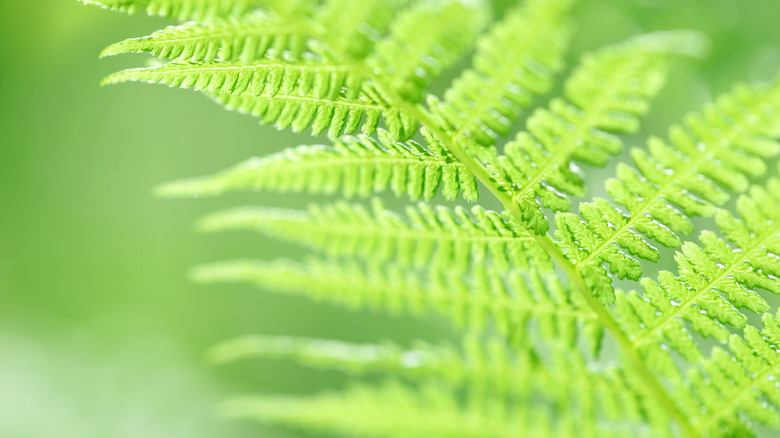
Fern extract
Did you know that the effects of the UV rays we are exposed to on a daily basis can contribute up to 80% of visible signs of aging? So by all means, continue donning that sun hat and slathering on the sunscreen. But what if there was a sunscreen pill that could also protect your skin from those harmful rays? It turns out, there is.
Polypodium leucotomos is the extract of a Central American fern plant. Studies published by The American Academy of Dermatology have shown that supplementing with the fern extract can provide the skin with lengthened exposure to UV rays before burning, as well as protect individuals with a condition called polymorphous light eruption, which causes those afflicted to suffer from itchy rashes when exposed to sunlight.
Dr. Henry W. Lim, chairman of the department of dermatology at Henry Ford Hospital, said in the article, "We're not completely sure how sunscreen pills work, but the main understanding is that polypodium leucotomos acts as an antioxidant, so it protects the skin from oxidative damage caused by sun exposure."
As sunscreen pills offer sun protection comparable to a level SPF three to five, Dr. Lim says, "If someone wants to take a sunscreen pill, they should continue protecting their skin by seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and applying sunscreen. While there have been promising results, more research needs to be done to know the optimal way of using these pills and their long-term safety."
Biotin
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin that makes itself at home amongst the B-complex family. It's also known as B7, and sometimes is referred to as its old name, vitamin H, or coenzyme R. Biotin has long been touted as a miracle supplement for the beauty of hair, skin, and nails, appearing as an ingredient in many over the counter beauty formulations. But does it live up to the hype?
The answer is debatable. A deficiency in biotin can lead to hair loss, brittle nails, and cause cradle cap in infants, indicating that this vitamin is indeed essential to the health of hair, skin, and nails. But deficiency of biotin is extremely rare, since it is found in many of the foods we likely eat often, like eggs, cheese, nuts, beans, and leafy greens. Our bodies are also capable of synthesizing a small amount of it per day.
Any excess of the water-soluble vitamin is excreted in our urine, and there are no known toxicity levels of biotin, making it a safe supplement to try out, but the truth is that very few studies show it makes any difference in individuals who are not deficient in the nutrient. The most promising studies indicate it will help with brittle nails, and mega doses are thought to be effective in treating multiple sclerosis.
Collagen
Collagen "is the most abundant protein in the human body." It provides the building blocks for bones, tendons, ligaments, teeth, muscles, and yes, the body's largest organ — the skin. Our bodies make collagen when we eat the proper amounts of certain minerals, vitamin C, and protein, but as we age, our bodies produce less and less, and we lose skin suppleness and firmness. So why not just supplement with collagen to beautify our skin?
Animal proteins, particularly bone broth, gelatin, and animal skin, are very high in collagen. But does eating more of them translate to more collagen in our bodies? What about all of the collagen supplements found in pills, powders, and beverages? The common criticism of collagen supplementation is that the collagen is broken down as soon as it hits the stomach. As dermatologist Dr. Karen Grossman explained to Vogue, it is difficult to determine how much of the collagen we ingest gets absorbed as collagen, and how much the body repurposes. She says, "More studies need to be done to help to figure out how these products may or may not be affecting our bodies."
But there have been promising studies that show that collagen supplementation can improve skin quality — provided you consume the right kind of collagen. Both hydrolyzed collagen and gelatin have been broken down into peptides that may be more bioavailable, with studies showing that they provide benefits when supplemented both orally and topically, improving skin elasticity and hydration.
What does it all mean for you?
Are you now excited to add some more nutritional supplements to your beauty regimen? Before you jump right into a bevy of new supplements, be sure to consider the following recommendations on choosing which supplements are right for you.
Quality is important when it comes to nutritional supplements, so seek out a trusted, reputable brand. The cheapest drug store vitamins are not always going to be the most effective. When purchasing herbal supplements, look for "standardized" formulations that contain a specific amount of the herb's desired compounds. High-quality herbal supplements will be certified by organizations like The United Natural Products Alliance, NSF International, or The United States Pharmacopeia.
With any supplement, consult your doctor if you are currently on any medications, as there are possible drug interactions with over the counter vitamin and herbal supplements. Once you embark on your supplementation process, remember, patience is a virtue. When taken consistently, it can take two to three months for you to see and feel the changes the supplement may bring you. But for your most gorgeous skin ever, it will certainly be worth it!