The Skincare Ingredients You Need If You Have Discoloration
We may receive a commission on purchases made from links.
As summer approaches, the days are getting longer and protecting your skin from UV rays becomes even more of a priority. While being out in the sun can give you a glowing tan, it can also cause patchy discoloration on the face. Women are especially prone to melasma, a form of hyperpigmentation caused by hormonal changes and sun exposure (via American Academy of Dermatology). While women of all skin tones and skin types are beautiful, skin discoloration can make some feel less confident in themselves. Luckily, there are several treatments available that can help reduce hyperpigmentation.
One standout ingredient is tranexamic acid (TA). TA, initially available in oral form, was originally used to treat blood clots (via InStyle). Now, it is additionally available in topical form and is also used to brighten hyperpigmentation. According to the Journal of Dermatological Science, TA inhibits the process of melanin production by blocking pigment from reaching the outer layer of the skin.
Miami-based dermatologist Roberta Del Campo told Allure, "This new ingredient is known to help not only lighten [hyperpigmentation] but decrease recurrence, which is crucial." Cosmetic dermatologist Tiina Meder told Glamour UK that TA can be used for the treatment of existing skin discoloration, including melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, in people of all skin types and shades. TA is an anti-inflammatory ingredient with calming properties, and can help repair the skin barrier. Unlike many skincare actives out there, TA actually decreases skin sensitivity to UV exposure.
A new gold standard in treating hyperpigmentation
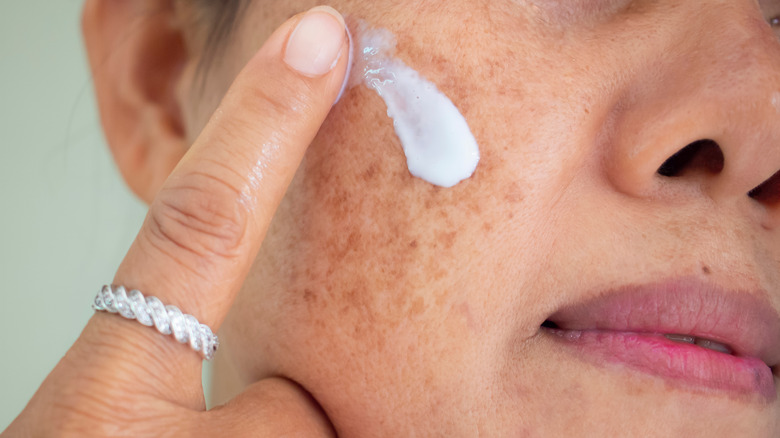
Hydroquinone is an effective dark spot treatment that is typically prescribed by dermatologists for patients with hyperpigmentation. Del Campo told Allure, "Hydroquinone is the gold standard for hyperpigmentation, as it works on the cells that make melanin to block further production." However, the ingredient is controversial as it can sometimes cause ochronosis, or darkened, blue-toned pigmentation with prolonged use, per Healthline. That's why it is only effective as a short-term treatment to be taken with breaks and not to be used continuously for more than five months at a time.
There's a safer alternative to hydroquinone — arbutin. Dr. Michelle Green, a New York City-based dermatologist, told Dermstore, "Arbutin is a natural form of hydroquinone derived from the bearberry plant. It is a safer and effective alternative to hydroquinone and is less cytotoxic to the melanocytes." Dermatologist Claire Chang explained to Shape, "It works by slowly releasing hydroquinone over time, inhibiting tyrosinase, the key enzyme responsible for the production of melanin, or pigment, in the skin." Chang said that arbutin is an antioxidant and has anti-inflammatory properties.
Unlike hydroquinone, there is no risk of irritation with arbutin and you can continue to use the ingredient in your routine, without taking a break. Dermatologist Ife Rodney told Shape, "Because the hydroquinone is being released slowly, the skin isn't exposed to too much of it any one time, mitigating the likelihood of those side effects."
Other ingredients with skin-brightening properties
Licorice has soothing properties and can help even out hyperpigmentation and lighten dark spots. Green told Dermstore, "Licorice root contains two ingredients that help with pigmentation: glabridin and liquiritin," elaborating, "Glabridin helps to retain tyrosinase, an enzyme that produces melanin, which leads to pigmentation. Liquiritin helps to break up and remove melanin and pigmentation in the skin."
Vitamin C can help boost the effects of TA, but it also helps brighten the skin on its own. Green told Dermstore, "Vitamin C is an amazing antioxidant that is beneficial for patients with hyperpigmentation." She added, "It works by brightening hyperpigmented spots on the skin, but not lightening normal skin." Additionally, vitamin C can boost the protective effects of sunscreen, per Baylor College of Medicine.
Speaking of sunscreen, it's important to wear plenty of it to prevent UV-related damage, which includes melasma. Dermatologist Shari Marchbein recommended wearing broad-spectrum SPF 30+ and told InStyle, "Remember that before you spend your money on antioxidant serums, brightening ingredients, and retinoids to improve the tone of your skin and hyperpigmentation, the most important and first step is diligent daily sun protection."
For people concerned about skin discoloration, dermatologist Dhaval Bhanusali recommends physical/mineral sunscreens over chemical sunscreens, as the latter could worsen skin discoloration (via Allure).